In most cases, weekdays could be so busy and bombarded that several people are left with no more time to work out. However, a study shows that weekend workouts that span at least 150 minutes may still be sufficient.
Weekday vs. Weekend Workouts
The study "Accelerometer-Derived "Weekend Warrior" Physical Activity and Incident Cardiovascular Disease" covered nearly 90,000 people. Findings reveal that moderate to vigorous physical activity, focused on one to two days in a week, could result in similar cardiovascular benefits as similar exercise amounts done throughout the entire week.
Dr. Shaan Khurshid, the study's lead author and a cardiologist from Massachusetts General Hospital, explains that getting exercise is more important than how much is gained. A weekend bike ride, run, brisk walk, or soccer match could all matter.
Dr. Keith Diaz, who is an exercise psychologist at the Irving Medical Center of Columbia University, noted before that studies have shown that quick strolls during the day could lead to great health impacts. Dr. Diaz noted that taking a light walk for five minutes every 30 minutes could offset several dangers that come with sitting. Prolonged periods of sitting could increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancer types.
Physical Activity Matters
With this, it is clear that regular physical activity is crucial for overall health. Aside from resulting in cardiovascular benefits, it can also boost brain health, strengthen muscles and bones, aid with weight management, and boost capacity for daily activities.
It is generally recommended that adults spend at least 150 minutes a week engaging in vigorous aerobic activity or a mix of moderate and vigorous activity. This can also be spread out over various days. To yield more health benefits, one can spend 300 minutes each week engaging in moderate aerobic activity.
Moderate aerobic activity includes biking, swimming, brisk walking, or even mowing the lawn. On the other hand, vigorous exercises include swimming laps, running, aerobic dancing, and doing heavy work in the yard.
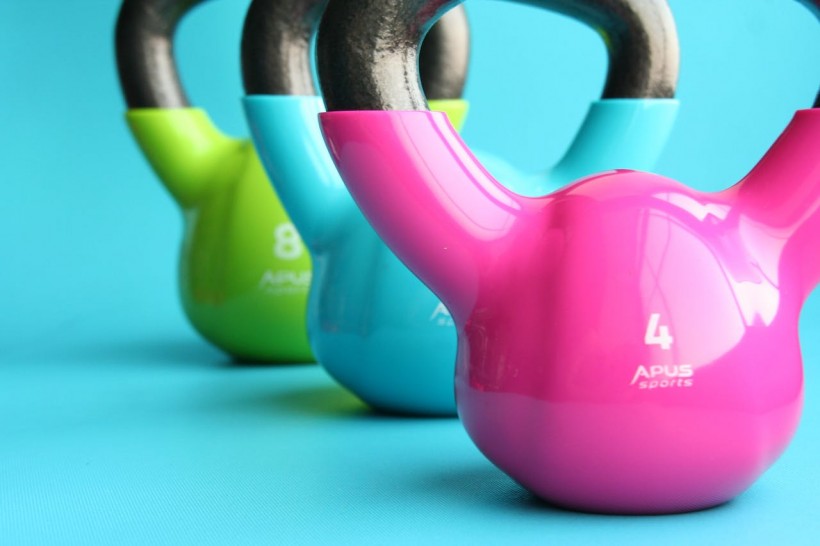
Aside from this, it is also recommended to engage in strength training exercises for various muscle groups at least twice a week. A single exercise set is sufficient for fitness and health benefits. Making use of resistance or weights that could tire the muscles after 12 to 15 repetitions is recommended.
Strength training can be done by using weights, machines, one's own body weight, resistance bands, or heavy bags.
It is also crucial to cut down on time spent sitting. Longer sitting hours lead to higher metabolic risks. Prolonged periods of sitting could negatively affect one's longevity and health even when one engages in the suggested amount of physical activity.
RELATED ARTICLE: Exercise as Serious Depression Treatment? Massive Study Suggests That Its Power Should Not Be Underestimated
Check out more news and information on Medicine & Health in Science Times.




![Earth's Quasi-Moon Kamo‘oalewa Could Originate From Lunar Surface Not Asteroid Belt [Study]](https://1721181113.rsc.cdn77.org/data/thumbs/full/53275/89/56/50/40/earths-quasi-moon-kamo-oalewa-could-originate-from-lunar-surface-not-asteroid-belt-study.png)









