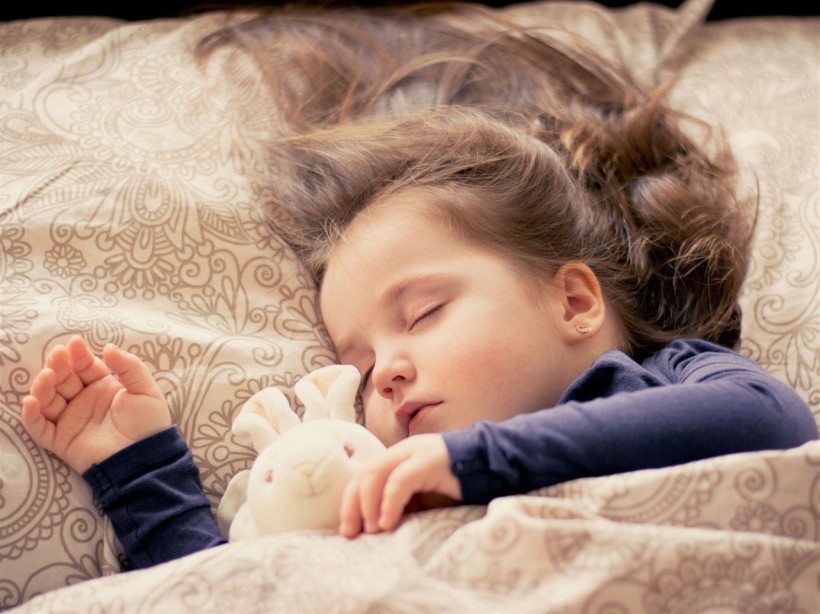
In common with other mammals, human beings sleep better in slightly cooler nighttime environments. Keeping your bedroom at a lower temperature (18-21C or 60-70F) reinforces natural sleep signals and rhythms. Bed and bedding materials are essential, with memory foam generally warmer than sprung mattresses or newer technologies like AirFoam. Being too warm means you may take longer to sleep or experience lower quality sleep.
Read on to find out more...
The science behind sleeping cool at night
The science behind sleeping cooler is surprisingly straightforward, and if you want to get a good night's sleep, it's definitely worth paying some attention to your mattress, bedding, and thermostat.
The thermoregulation mechanism of the human body is strongly linked to the mechanism regulating sleep. This makes the thermal environment key to a good night's sleep, with room temperature and bed temperature both contributing.
Why do you sleep better at night in cooler temperatures
Falling asleep is characterized by a drop in core body temperature. As internal temperatures decline, humans and other animals tend to engage in "nesting" behaviors that lead to sleep, such as wrapping up in a blanket, lying down, and closing our eyes.
The most pronounced fall in core body temperature occurs at the REM (rapid-eye-movement) sleep phase. This is the stage of deep sleep where dreams typically occur. Once we enter a phase of non-REM sleep, the brain also cools.
Ignoring instincts or physical cues around temperature, lighting, and tiredness can make it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. You can improve the ability to fall asleep by warming your skin through a bath or shower an hour or two before bed. The heat stimulation causes the body to react and cool you down via vasoconstriction, settling at an ideal sleeping temperature.
As well as supporting the natural fall in body temperature which precedes sleep, cooler temperatures also stimulate the production of two hormones associated with sleep and overall health.
Melatonin supports sleep and also has a hypothermic effect, decreasing body temperature in a mutually reinforcing pattern. HGF (Human growth hormone) is a vital hormone produced by the pituitary gland in the brain and reaches maximum levels during phases of deep sleep.
Why AirFoam is cooler than other materials
If you find yourself frequently overheating at night, your mattress or bedding could be part of the problem. Mattresses and bedding can be made from a range of natural and synthetic materials, all of which behave differently in terms of absorbing or releasing heat.
Most mattresses will use some variety of traditional spring or coil design, memory foam, or a hybrid of these. Newer cooling technologies are also coming onto the market, including AirFoam, Gel Foam and Open Cell Foam.
Standard memory foam mattresses or mattress toppers can feel particularly hot. This type of foam is formed from a dense, synthetic material designed for softness and support rather than efficient ventilation and moisture absorption.
In contrast to traditional memory foam, AirFoam is a newer temperature-neutral material, which doesn't trap heat. When used in mattress construction AirFoam can help build a cooler sleep environment.
A final word...
Investing in sleep-enhancing items like a cooling mattress or pillows, natural bedding and a bedroom thermometer could help you experience more restful nights and more energized days. Depending on your needs, you should also check out cotton, linen or bamboo sheets.
Overall, what should you do if you're finding your bedroom too hot to handle? To sleep well, stay cool...
* This is a contributed article and this content does not necessarily represent the views of sciencetimes.com