Climate change can lead to rising sea levels which may affect multiple countries, especially those that are surrounded by shorelines. In recent years, data recorded from more than a decade were compared to analyze the future of rising sea levels around the globe. But even though we obtained predictions of the increase in seawater, what lies beneath the melting ice sheets is still a mystery for the science community.
2023 Robotic Voyage in Greenland
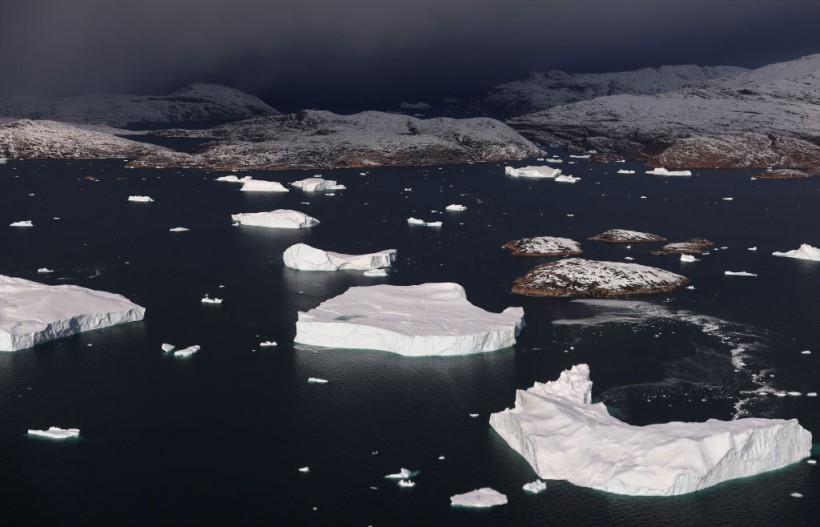

UPERNAVIK, GREENLAND - SEPTEMBER 07: Icebergs are seen from NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) research aircraft on September 7, 2021 near Upernavik, Greenland. The NASA Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) campaign is wrapping up a six-year mission studying the ocean and glaciers along Greenland’s 24,000 mile remote coastline with airborne and shipborne instruments- data which cannot be captured by satellite. Each summer, OMG releases around 250 ocean probes from a modified DC-3 aircraft into the ocean to monitor the temperature and salinity of Atlantic subsurface waters around Greenland. According to NASA, the goal of the mission is ‘to figure out how much of Greenland’s ice melt is caused by warming oceans.’ Greenland’s massive ice sheet holds enough water to raise sea levels by around 25 feet worldwide.
In 2023, experts aim to discover the vast, untapped world under the wide glaciers in the northern hemisphere. The exploration will be administered by scientists from the University of Texas at Austin.
A submersible robot will be developed for the voyage under three glaciers located in Greenland. The project will be the first attempt to dive into the deepest regions of the cold waters beneath the country's biggest ice masses. The set of glaciers subjected to the study is considered the second largest ice sheet on our planet.
The Greenland ice sheet study will be made in part by the efforts of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI). The underwater vehicle selected for the mission is the Nereid Under Ice (NUI).
The submarine was specialized to surpass the harsh conditions under the ice sheet. The vehicle is expected to withstand riptides and maneuver between towering icebergs underwater, while successfully withdrawing data and samples from the mysterious environment.
ALSO READ: Climate Change Could Be Delayed? Mechanical Trees Could Absorb Carbon Dioxide Tell Us How
Climate Change, Rising Sea Levels, and Moraines Among Exploration's Interest
Among the interests of the glacier voyage is the natural sand walls called moraines. These materials are theorized to have the capacity to maintain the structure of glaciers and hold the entirety of the vast ice sheets. Anticipated results from the research include a set of factors that support the glaciers in Greenland, and the scale needed for them to ultimately break.
University of Texas Jackson School of Geosciences expert Ginny Catania said in a EurekAlert report that all of the findings would support the wider efforts to accurately predict the impact of rising sea levels. Through the study, the team will get ahold of the exact volumes contained in the ice sheet, and how much increase and speed it would take for the melting glaciers to reflect on the global sea levels.
Alongside the climate change crisis, the study beneath Greenland's ice sheets will provide a contribution to the future of geoengineering projects. Artificial moraines are being eyed in the community today, as they believe that it can help the world buy more time amidst the gradual efforts in reducing carbon energy.
NUI submarine will defy the icebergs and riptides to have complete seafloor mapping under Greenland's glaciers. It will be guided and controlled remotely by ships nearby the target site.
WHOI senior engineer and project co-lead Mike Jakuba said in a UT News report that the robot was built with layers of redundancy. It was equipped with battery packs, multiple thrusters, and a navigation system, all-sufficient for automated operation.
The exploration, which will commence in midsummer 2023, is funded by the prestigious W.M. Keck Foundation. The three glaciers selected for the project are the Kangilliup Sermia, Umiammakku Sermiat, and the Kangerlussuup Sermia.
RELATED ARTICLE: Climate Change Affects Coffee Quality and Turn Your Favorite Morning Brew Into A Luxury Product, Study Says
Check out more news and information on Climate Change in Science Times.



![Earth's Quasi-Moon Kamo‘oalewa Could Originate From Lunar Surface Not Asteroid Belt [Study]](https://1721181113.rsc.cdn77.org/data/thumbs/full/53275/89/56/50/40/earths-quasi-moon-kamo-oalewa-could-originate-from-lunar-surface-not-asteroid-belt-study.png)