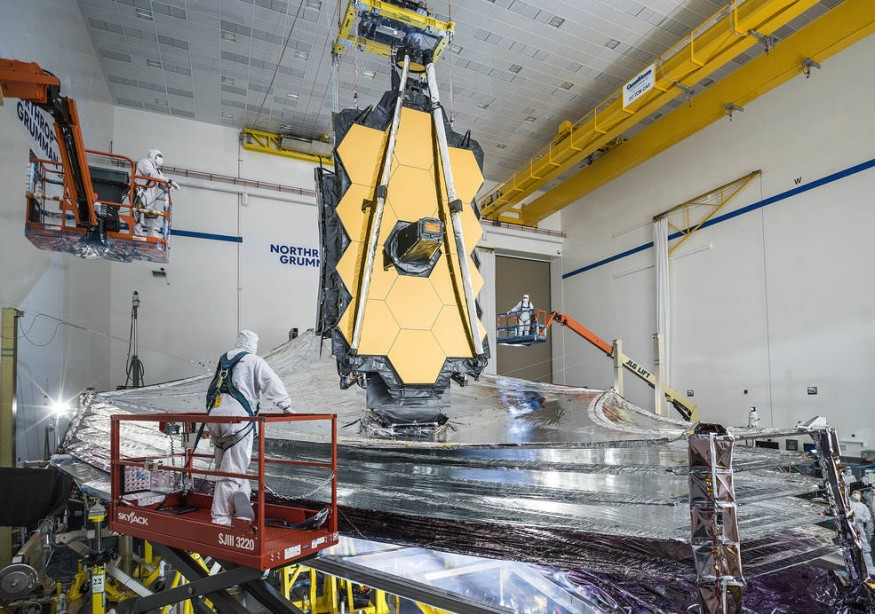
The James Webb Telescope has been fitted with a massive heat shield by NASA engineers in preparation for its launch later this year.

Like the Hubble Space Telescope, Webb will be launched into space to take photographs of the stars without even peering into the Earth's atmosphere.
On the other hand, Webb would orbit our sun at a distance of about a million miles, while Hubble orbits the Earth at a distance of about 347 miles.
What Does the Sunshield Look Like?
NASA said the sun shield, a five-layer diamond-shaped device the size of a tennis court, was specially designed to fold up along the telescope's two sides.
The sun shield will remain in this lightweight state through launch for the first few days the observatory will spend in orbit now that folding has been completed at Northrop Grumman in Redondo Beach, California.
The sun shield took a month to fold, and its five layers are incredibly thin; four of them are just 0.001 centimeters thick.
The shield is also very wide, measuring 70 by 47 feet-roughly the tennis court's size. It must be explicitly folded to fit into the 18-foot diameter payload part of the Ariane 5 rocket that will propel it into space and unfurl it.
The primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope measures 7 feet, 10.5 inches long.
The shield would re-open in precisely the right way at the end of Webb's first week in orbit. For this to happen, 107 pins must be released, as well as 90 separate tensioning cables.
Jeff Cheezum, a lead engineer at aerospace and defense company Northrop Grumman, said in a statement that Webb's sun shield must be properly stowed - much as a skydiver's parachute must be packed accurately to open safely and safely return to Earth - to hold the telescope at its required working temperature.
Newsweek said one side of the shield will always face the Sun, while the other will always face away, to keep the telescope cool. The hot side will experience temperatures as high as 230 degrees Fahrenheit. In comparison, the cold side will experience temperatures of about -394 degrees Fahrenheit.
When Will They Stow Webb's Sun Shield?
The sun shield is one of Webb's most essential and dynamic elements, designed to protect the telescope's optics from any heat sources that might interfere with its vision.
Webb, an infrared telescope, is expected to hold its mirrors and sensors at incredibly low temperatures to sense weak heat signals from far away objects.
Engineers will now spend three months before launch stowing the ready sun shield. NASA announced in July of last year that the mission will take place on October 31, 2021. Webb will take off from French Guiana.
The James Webb Telescope will study galaxies more than 13 billion light-years from Earth. It needs a large mirror to absorb its faint infrared radiation. It is the largest spacecraft ever launched, measuring 21 feet 4 inches across.
RELATED ARTICLE : Space Missions in 2021: Here are The Most Exciting Events To See
Check out more news and information on Space on Science Times.
© 2026 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.