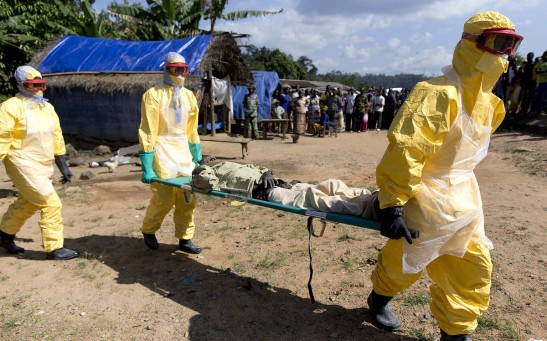
Ebola Virus
In the Wake of Ebola—H7N9 Influenza Has Spread in Secret
What Tactics Can Help You Survive A Zombie Apocalypse? Researchers Have the Answer
How Arachnids May Reveal Looming New Threats to American Public Health—Bourbon Virus

When It Comes to Pandemics and Outbreaks, Could Climate Change Be to Blame?
Healthcare Workers Attacked in Guinea as Locals Give Ebola the Upper Hand

Experimental ZMapp Treatment Off To Liberia to Begin Clinical Trials

Ebola Virus Shuts Down Ohio Bridal Shop in Wake of US Deaths

Biological Warfare on the Horizon? ISIS Soldiers May Be Infected With Ebola

FDA Approves a Fast-Acting Ebola Test

Could Killing the Bats End New Ebola Transmission? Why Death Won’t Work

Health Officials Believe They May Have Found Source of Newest Ebola Outbreak

FDA Approves New Roche Ebola Test For Emergency Use

Lab Error Leads CDC to Suspect Health Officials May Be Infected With Ebola

Can the Blood of Survivors Help Cure Ebola? The Limitations and Expectations of a New Vaccine
Most Popular

Worst ‘Cannibal’ Solar Storm in 165 Years Expected to Crash Into Earth’s Atmosphere Tonight Causing GPS, Power Outages

Cave of Death in Costa Rica Appears Harmless but Can Instantly Kill Anyone at the Entrance
Kinetic Magnetism: Quantum Motion of Atom Gives Rise to New Mechanism for Attraction and Repulsion

Space Weather Alert: NOAA Warns of a Solar Radiation Storm With 60% Chance of Hitting the Earth This Week