Anti-nutrients are the exact opposite of nutrients. Whereas nutrients are important for a living organism to grow and be healthy, anti-nutrients block the absorption of nutrients. Public Health Nutrition Assistant Professor Jill Joyce of Oklahoma State University explained the pros and cons of consuming anti-nutrients.
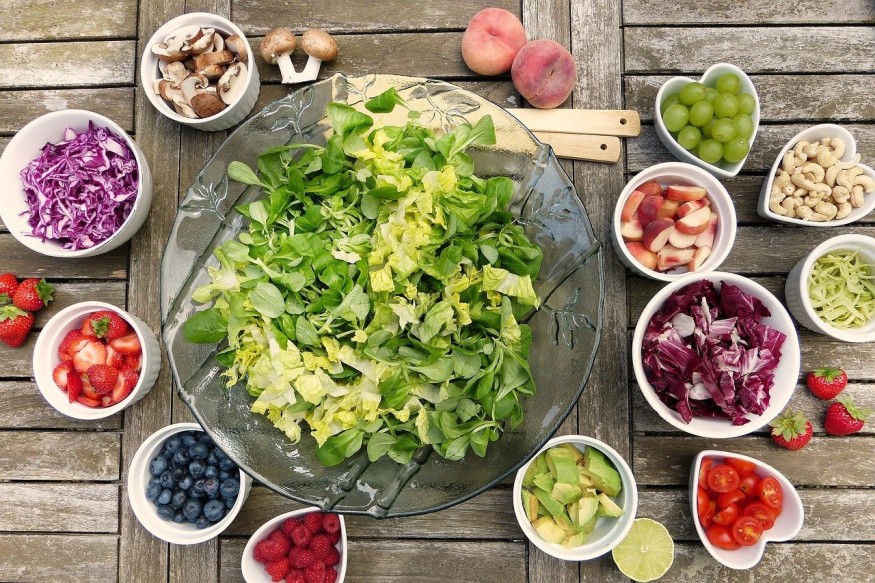

Anti-Nutrients Defined
Anti-nutrients are naturally found in plants and animal foods. The name speaks for itself because it blocks the absorption of nutrients into the body. That means anti-nutrients could decrease the number of nutrients that a person could get from the food, Joyce wrote.
Anti-nutrients usually interfere with the absorption of calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, and zinc. In plants, they are used as a defense mechanism against bacteria, fungi, insects, and parasites.
On the other hand, some anti-nutrients also work as survival tactics that help plant species grow and spread. They block the digestion of seeds that then come out of the animals as part of the fecal matter that can go on and grow.
While in humans, anti-nutrients are usually found in legumes and whole grains.
Examples of Anti-Nutrients
According to Harvard T. H. Chan, there are several examples of anti-nutrients. Here are some of it:
- Lectins are found in legumes, like beans, peanuts, and soybeans, and also in whole grains. Lectins interfere with the absorption of zinc, phosphorus, iron, and calcium.
- Oxalates are found in green leafy vegetables, as well as in tea leaves. Oxalates can bind to calcium and prevent it from being absorbed by the body.
- Glucosinolates can be found in broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, and other cruciferous vegetables. They prevent the absorption of iodine that could interfere with thyroid function. Those with goiter or iodine deficiency is at most susceptible.
- Phytates (phytic acid) are also present in whole grains, seeds, legumes, and some nuts. It decreases the absorption of calcium, iron, manganese, and zinc.
- Saponins are found in legumes and whole grains that could interfere with normal nutrient absorption.
- Tannins are present in tea, coffee, and legumes that also decrease absorption of iron.
Pros Outweigh the Cons
Although anti-nutrients have many cons, as it prevents the absorption of nutrients, its pros still outweigh them. Joyce said that foods containing anti-nutrients should still be encouraged to eat and not avoided because it only becomes a concern when a person consumes an ultra-high amount of anti-nutrients, which is unlikely.
Moreover, many nutrients also are removed from the foods as it is being processed and cooked, especially if they are soaked, blanched, boiled, or other high-heat processing.
ScienceAlert reported that vegetarians and vegans have a higher chance of experiencing the adverse effects of anti-nutrients because they mainly eat fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. These are foods that anti-nutrients are mostly found.
On the other hand, their diet is also considered as one of the healthiest diets because they have a lesser chance of developing cardiovascular diseases, obesity, diabetes, and cancers.
But vegetarians and vegans can still take a few steps to counteract the adverse effects of anti-nutrients in the food that they usually eat.
Check out more news and information on Nutrition on Science Times.
© 2026 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.